Pulmonary Lobe Segmentation with Probabilistic Segmentation of the Fissures and a Groupwise Fissure Prior
Unsupervised segmentation of the pulmonary lobes
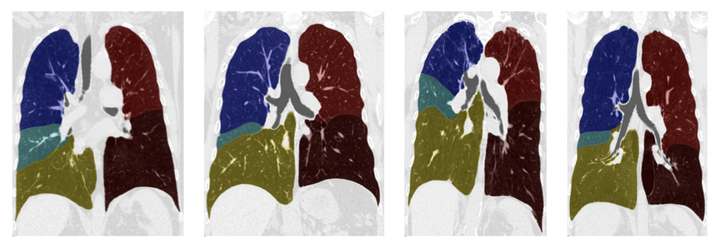 Lobe segmentations
Lobe segmentationsAbstract
A fully automated, unsupervised lobe segmentation algorithm is presented based on a probabilistic segmentation of the fissures and the simultaneous construction of a population model of the fissures. A two-class probabilistic segmentation segments the lung into candidate fissure voxels and the surrounding parenchyma. This was combined with anatomical information and a groupwise fissure prior to drive non-parametric surface fitting to obtain the final segmentation.
The performance of our fissure segmentation was validated on 30 patients from the chronic obstructive pulmonary disease COPDGene cohort, achieving a high median F 1 -score of 0.90 and showed general insensitivity to filter parameters. We evaluated our lobe segmentation algorithm on the Lobe and Lung Analysis 2011 dataset, which contains 55 cases at varying levels of pathology. We achieved the highest score of 0.884 of the automated algorithms.
Our method was further tested quantitatively and qualitatively on 80 patients from the COPDgene study at varying levels of functional impairment. Accurate segmentation of the lobes is shown at various degrees of fissure incompleteness for 96% of all cases. We also show the utility of including a groupwise prior in segmenting the lobes in regions of grossly incomplete fissures.